Healthcare Breach Alert: Protect Your Data Now
A healthcare data breach occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to protected health information (PHI), compromising its confidentiality, integrity, or availability. These breaches have escalated dramatically as healthcare providers have transitioned from paper charts to digital records, creating new vulnerabilities in the process.
What makes these attacks particularly concerning is the comprehensive nature of the data stored in electronic health record systems. Not just medical histories but also social security numbers, insurance information, and payment details. Unlike credit card information that can be changed after a breach, your medical history is permanent. Once exposed, this information can be used for insurance fraud, identity theft, or even blackmail.
If you're concerned about the security of your healthcare data and want to ensure that your information is protected, consider Tekkis. Our advanced solutions are designed to safeguard protected health information (PHI) and enhance your organization's data security. Don’t wait until a breach happens. Contact Tekkis today to learn more about how we can help you secure your healthcare data and keep your patients’ information safe.
Also Read:
Notable Healthcare Breaches: A Historical Overview
The healthcare industry's digital transformation has unfortunately been accompanied by increasingly severe data breaches. Both the frequency and scale of breaches have grown dramatically over the past decade, with financial impacts that are truly staggering.

According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report, healthcare breaches cost an average of $10.93 million per incident in 2023—significantly higher than any other industry. More concerning still, detection times often exceed 200 days, giving attackers ample time to extract and exploit sensitive information.
The Largest Healthcare Data Breaches of All Time
The scope of the largest healthcare data breaches illustrates the industry's vulnerability:
Case Study: Anthem Breach (2015) In what was then the largest healthcare breach in history, Anthem suffered a sophisticated phishing attack that compromised 78.8 million patient records. Attackers gained administrator credentials and accessed unencrypted data for months before detection. The aftermath included a $115 million settlement and a comprehensive corrective action plan that transformed the organization's security approach.
AMCA Breach (2018-2019) The American Medical Collection Agency breach affected over 20 million patients across multiple healthcare providers, demonstrating how third-party vendors can become dangerous weak links in the security chain. The breach ultimately led to AMCA's bankruptcy filing—a stark reminder of the existential threat these incidents can pose to businesses of any size.
Recent Major Breaches in 2024
The biggest data breach 2024 has witnessed so far is unquestionably the massive attack on Change Healthcare, a UnitedHealth Group subsidiary. This February 2024 ransomware attack potentially exposed the data of approximately 190 million individuals—over half the U.S. population—while simultaneously disrupting healthcare payments nationwide.
Recent healthcare data breaches have increasingly targeted integrated delivery networks and their critical infrastructure. The Lurie Children's Hospital in Chicago experienced a devastating attack in January 2024 that forced systems offline for weeks.
Root Causes of Healthcare Data Breaches
Understanding the main causes of healthcare data breaches requires looking beyond individual incidents to identify systemic vulnerabilities. Healthcare organizations face a unique combination of challenges: they manage extremely valuable data, often with limited IT resources, while maintaining complex systems that must remain operational 24/7 to support patient care.
According to healthcare cybersecurity statistics published by the Department of Health and Human Services, the number of reported breaches has increased by over 300% in the past decade. The sensitivity and comprehensive nature of healthcare data make it particularly valuable on darknet markets, where complete medical records can sell for up to $1,000 each—significantly more than credit card information.
Common Attack Vectors in Healthcare
Hacking in healthcare has evolved from opportunistic attacks to sophisticated operations often backed by organized criminal groups or even nation-states. The most prevalent attack vector continues to be phishing, accounting for approximately 57% of healthcare breaches according to recent studies.
Ransomware represents another devastating threat, with attacks increasing by 93% in 2023 alone. Modern ransomware operations employ a double-extortion model, both encrypting data and threatening to publish stolen information unless payment is made.
Case Study: Northeast Medical Group Response
Northeast Medical Group (name changed) successfully contained a ransomware attack in 2023 by implementing network segmentation that isolated critical clinical systems from compromised administrative networks.
Third-party vendor compromises have also emerged as a critical weakness, with business associates involved in approximately 43% of all healthcare breaches. When vendors with access to protected health information suffer security failures, multiple healthcare organizations often experience simultaneous data exposure.
Impact of Healthcare Breaches
The consequences of data breaches in healthcare extend far beyond the immediate exposure of sensitive information. These incidents create ripple effects that impact healthcare organizations, patients, and the broader healthcare ecosystem for years after the initial compromise.

Healthcare data breach statistics reveal a sobering reality: the sector experiences the highest per-record breach costs at $512 per compromised record—roughly double the cross-industry average. This dramatic difference reflects the comprehensive nature of medical records, which typically contain everything from personal identifiers to detailed health histories.
Financial and Reputational Costs for Organizations
The financial impact of healthcare breaches is staggering. According to IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report, healthcare organizations face an average total cost of $10.93 million per incident—nearly double the cross-industry average of $4.45 million. These expenses include:
- Immediate breach response (investigation, containment, remediation)
- Notification requirements
- Credit monitoring for affected individuals
- Legal fees and settlements
- Regulatory penalties up to $1.9 million per violation category annually
A 2023 survey revealed that 62% of patients would consider switching providers following a data breach, representing a potentially catastrophic loss of business. This reputational damage typically persists long after technical remediation is complete.
Consequences for Patients and Data Security
For patients, the consequences extend far beyond mere inconvenience. Unlike credit card theft, medical identity theft places significant burdens on victims. Resolving medical identity theft takes an average of 600 hours of personal effort—roughly equivalent to 15 weeks of full-time work.
Data breach statistics show that 22% of healthcare breach victims experience some form of identity theft within two years of the incident. Medical identity theft allows criminals to receive care under the victim's name, potentially corrupting their medical records with inaccurate information about allergies, conditions, or treatments—creating dangerous clinical scenarios.
Regulatory and Legal Frameworks
Healthcare organizations operate under one of the most comprehensive regulatory environments in the United States, with multiple overlapping frameworks designed to protect sensitive patient information.
Role of HIPAA in Mitigating Breaches
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) serves as the cornerstone of healthcare data protection in the United States. The Security Rule requires organizations to implement appropriate administrative, physical, and technical safeguards based on their specific risk profiles.
HIPAA statistics reveal the regulation's significant impact: organizations with comprehensive HIPAA compliance programs experience 35% fewer breaches than those with minimal programs. This correlation demonstrates how the framework's structured approach to security management helps prevent incidents before they occur.
Fines and Penalties Imposed by OCR and FTC
Enforcement provides the regulatory framework with essential teeth. The HHS Office for Civil Rights (OCR) has imposed over $131 million in HIPAA penalties since enforcement began. These penalties range from $127 to $63,973 per violation, with annual caps of $1.9 million per violation category.
The largest HIPAA settlement to date involved Anthem Inc., which paid $16 million following a breach affecting nearly 79 million people. This record-setting case demonstrated OCR's willingness to pursue substantial penalties proportionate to the scale and impact of breaches.
Best Practices for Preventing Healthcare Data Breaches
Understanding how to prevent data breaches in healthcare requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both technical vulnerabilities and human factors.

Implementing Strong Cybersecurity Measures
Effective security begins with comprehensive risk assessment and management. Organizations should implement:
- Defense-in-depth approach: Deploy multiple overlapping protections rather than relying on a single security layer
- Network segmentation: Isolate critical clinical systems from general administrative networks
- Strong access management: Implement role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication, which can reduce unauthorized access risks by 99.9%
- Encryption: Implement both in-transit and at-rest encryption for all systems containing protected health information
- Continuous monitoring: Deploy security information and event management (SIEM) platforms to rapidly detect suspicious activities
- Third-party risk management: Conduct comprehensive vendor security assessments and ongoing monitoring
Case Study: Midwest Regional Health System
After experiencing a minor breach in 2022, Midwest Regional Health System (name changed) implemented a comprehensive security transformation. Their approach combined technical controls with organizational changes, including board-level security oversight and integration of security requirements into all technology procurement. Within 18 months, they documented a 67% reduction in security incidents and successfully repelled a ransomware attempt that targeted several peer organizations in their region.
Staff Training and Awareness Programs
Technology alone cannot prevent breaches—human factors play a critical role in maintaining security. Studies consistently show that organizations with robust security training experience 70% fewer successful phishing attacks than those without such programs.
Effective training approaches include:
- Role-specific training tailored to healthcare's unique context
- Regular simulated phishing exercises with educational follow-up
- Micro-learning approaches that deliver brief, frequent security reminders
- Clear reporting mechanisms for security concerns
- Regular security updates about current threats
Responding to a Breach: Patient Action Plan
If you receive notification that your healthcare information was involved in a data breach, take these immediate steps:
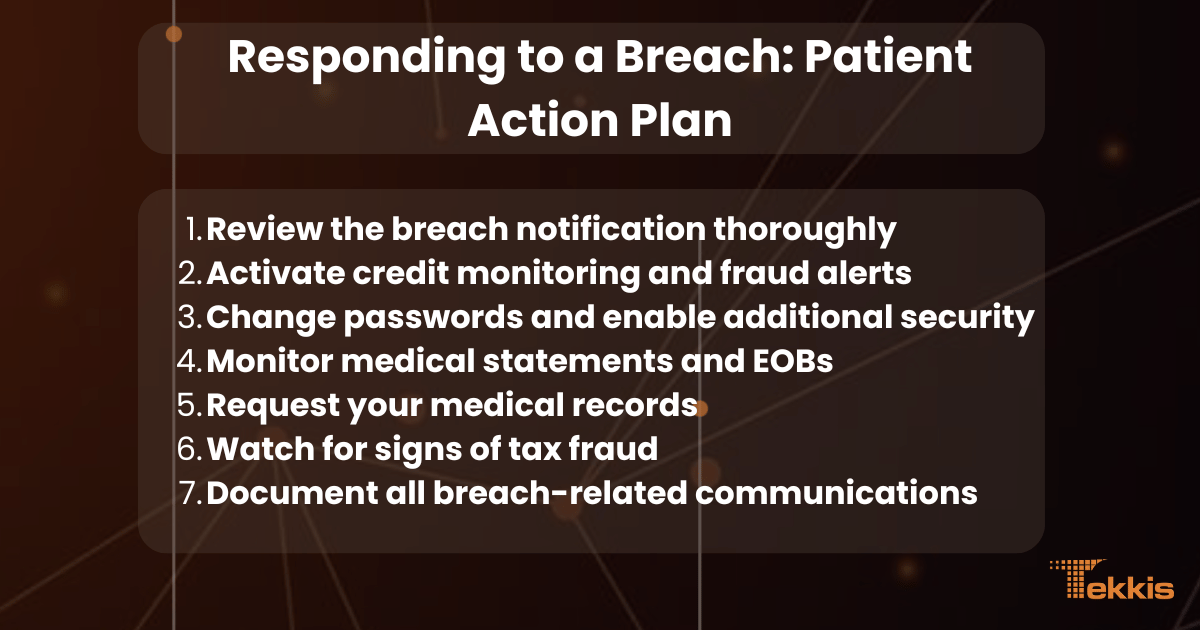
7-Point Actionable Checklist for Patients
-
Review the breach notification thoroughly
- Identify exactly what information was exposed (medical records, Social Security number, payment information)
- Note the timeframe when the breach occurred
- Document any offered remediation services (credit monitoring, identity protection)
-
Activate credit monitoring and fraud alerts
- Enroll in any free credit monitoring services offered by the breached organization
- Place a fraud alert with all three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, TransUnion)
- Consider placing a credit freeze for maximum protection
-
Change passwords and enable additional security
- Update passwords for your patient portal accounts, insurance websites, and any healthcare-related services
- Enable multi-factor authentication wherever available
- Use unique passwords for each healthcare service
-
Monitor medical statements and EOBs
- Carefully review all Explanation of Benefits (EOB) documents from your insurance company
- Look for medical services you didn't receive or providers you haven't visited
- Report any suspicious activity to your insurance company immediately
-
Request your medical records
- Obtain copies of your medical records from major providers
- Review for any treatments, diagnoses, or prescriptions you haven't received
- Request corrections for any inaccuracies you discover
-
Watch for signs of tax fraud
- File your tax returns early to prevent fraudsters from filing in your name
- Respond immediately to any IRS notices about duplicate tax filings
- Consider obtaining an IRS Identity Protection PIN
-
Document all breach-related communications
- Keep copies of all breach notifications and response actions
- Maintain a log of all calls or emails related to the breach
- Track any expenses incurred while addressing the breach (may be reimbursable)
Understanding Your Legal Rights
As a patient affected by a healthcare data breach, you have specific rights under federal and state laws:
- The right to be notified of breaches involving your unsecured protected health information
- The right to obtain a copy of your medical records to check for inaccuracies
- The right to request corrections to your medical records
- The right to file complaints with the HHS Office for Civil Rights and your state attorney general
- Potential right to join class action lawsuits against the breached organization (varies by situation)
FAQs and Additional Resources
Common Questions About Healthcare Data Breaches
Healthcare breaches commonly expose demographic information (names, addresses, dates of birth), financial data (billing information, credit card details, insurance information), medical records (diagnoses, treatment plans, medication lists), and Social Security numbers. Recent healthcare data breaches have increasingly targeted complete medical records rather than isolated data elements.
Under HIPAA regulations, covered entities must notify affected individuals within 60 days of discovering a breach. However, HIPAA statistics show that organizations increasingly provide notifications more quickly—typically within 30 days. State laws may impose stricter timelines, with some requiring notification within 30 or even 15 days.
Take immediate action by following the 7-point checklist in this article. Pay particular attention to monitoring both your financial accounts and medical records, as healthcare breaches can lead to both financial fraud and medical identity theft.
While HIPAA does not provide a private right of action (meaning individuals cannot sue directly for HIPAA violations), many successful lawsuits have been filed under state laws regarding negligence, breach of contract, or violation of state-specific privacy regulations. Class action lawsuits frequently follow major healthcare breaches.
Identity theft protection services can provide valuable monitoring and recovery assistance, but they cannot prevent all forms of misuse. These services are most effective at detecting financial identity theft but may not catch medical identity theft. Regularly reviewing your medical records and explanation of benefits documents remains essential even with protection services in place.
Where to Learn More and Get Further Assistance
Government Resources
- The HHS Office for Civil Rights maintains a comprehensive resource center at www.hhs.gov/hipaa with guidance for both organizations and individuals regarding HIPAA compliance and rights.
- The Federal Trade Commission offers detailed guidance for identity theft victims at identitytheft.gov, including specialized information about medical identity theft.
Industry Organizations
- The Health Information Management Systems Society (HIMSS) publishes regular reports and resources on healthcare cybersecurity at www.himss.org/resources/cybersecurity-healthcare.
- The National Health Information Sharing and Analysis Center (NH-ISAC) at www.h-isac.org offers threat intelligence specifically focused on healthcare security threats.
Consumer Protection Organizations
- The Privacy Rights Clearinghouse maintains a comprehensive guide to health information privacy at privacyrights.org/consumer-guides/health-privacy.
- The World Privacy Forum offers specialized resources about medical identity theft at worldprivacyforum.org/medical-identity-theft.
Staying informed about emerging threats and best practices represents one of the most effective ways to protect sensitive healthcare information. By regularly consulting these resources and implementing recommended security measures, both individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their breach risk.



